Diabetes can have several impacts on hair and scalp health due to its effects on blood circulation, hormone levels, and immune function. Here are some key ways diabetes can affect your hair and scalp:
1. Hair Thinning and Loss: Poor blood circulation associated with diabetes can limit the delivery of essential nutrients to hair follicles, potentially leading to hair thinning or hair loss. This can affect not just the scalp but other parts of the body as well.
2. Slower Hair Growth: People with diabetes may notice that their hair grows more slowly than before. This reduced growth rate is linked to impaired nutrient supply and chronic inflammation in the body.
3. Scalp Infections and Dryness: Diabetes can make the scalp more prone to infections and dryness due to higher blood sugar levels that create an ideal environment for yeast and bacteria growth. This can lead to dandruff or other scalp conditions.
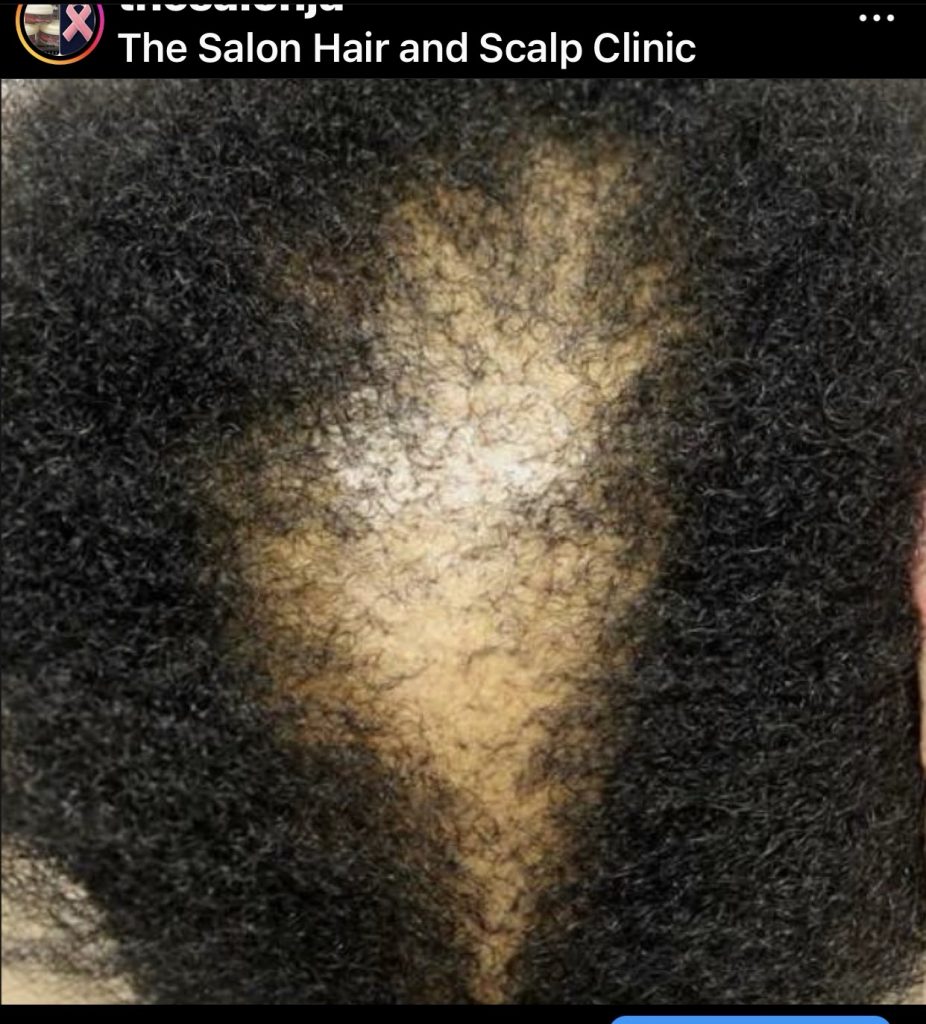
4. Alopecia Areata: Diabetes, particularly Type 1, is associated with autoimmune disorders like alopecia areata, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, resulting in patchy hair loss.
5. Increased Shedding: Diabetic individuals may experience telogen effluvium, a temporary condition where hair sheds more than usual due to stress or illness, which can be more common with fluctuating blood sugar levels.
Maintaining good blood sugar control, a healthy diet, and a proper hair care routine can help mitigate these effects. If hair loss or scalp issues persist, consulting with a trichologist or healthcare professional is advised.